
As immigration continues to grow in Europe, the conflict over resource allocation between immigrants and local residents has become a focal point of social concern.
This conflict primarily manifests itself in areas such as public resources, employment opportunities, and social welfare, particularly in economically constrained countries or regions, where competition for resources is more pronounced. How to effectively mitigate this conflict and promote harmonious coexistence between immigrants and local residents is a major issue that European governments urgently need to address.
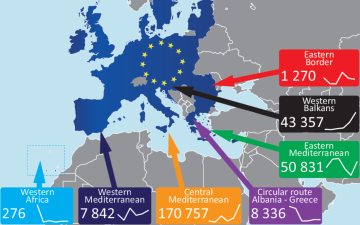
EU Immigration Situation
As the world's most integrated regional organization, the free movement of people between member states is a fundamental right within the EU. However, with the increasing number of refugees and illegal immigrants, EU countries face significant challenges in immigration management.
- Increased numbers: According to the latest data from Eurostat, the number of immigrants from Africa and Asia increased by 20% in 2022 compared to the previous year, and this trend appears unlikely to be reversed in the short term.
- Diversity: Immigrants to the EU come not only from Africa and Asia, but also from other European countries and the Americas. This diverse immigrant background presents new challenges for social integration and management in various countries.
- Illegal Immigration: As the number of immigrants increases, the problem of illegal immigration is also becoming increasingly serious. Some individuals enter EU countries through smuggling, hiding, and other means, placing tremendous pressure on national security and border management.
Impact of EU Immigration
Immigration in the EU has had a profound impact on governments and societies, primarily in the following areas:
- Economic: The arrival of immigrants has injected new vitality into the EU's economic development, filled gaps left by an aging population, and promoted competition in the labor market. However, some countries face fiscal pressures and social welfare allocation issues due to accepting large numbers of immigrants.
- Political: Immigration has become a sensitive issue in European politics. Populist parties in some countries have exploited anti-immigration rhetoric to gain voter support, creating instability in the European political landscape.
- Socio-Cultural: Immigration has enriched the EU's multicultural society, but it has also led to some social tensions and conflicts. For example, some local residents harbor concerns about immigrants' cultural customs and religious beliefs, which can even spark feelings of rejection.
Social Welfare Distribution
Most European countries have robust social welfare systems, which have become a key factor in attracting immigrants. When immigrants become increasingly reliant on social welfare systems, local residents often worry that their welfare rights are threatened. Some local residents believe it's unfair that immigrants receive the same benefits as them without having to pay taxes for a long time, exacerbating conflicts between immigrants and local residents.
In some countries with high immigration rates, the pressure on social welfare has even sparked political backlash, with some populist parties exploiting this to stoke anti-immigrant sentiment and advocate for restricting immigrants' access to social resources. This not only affects the relationship between immigrants and local residents but also, to a certain extent, undermines social cohesion and stability.
To address the EU's immigration issues, the following strategies are worth considering:
- Policy: Governments should strengthen communication and cooperation, formulate unified immigration policies, balance the interests of all parties, and ensure that the burden of immigration is equitably shared. At the same time, they should intensify efforts to combat illegal immigration and reduce its root causes.
- Legal: Improve relevant laws and regulations to protect the legitimate rights and interests of immigrants, while strengthening legal sanctions against illegal immigration and human trafficking. Strengthen judicial cooperation to jointly combat transnational crime.
- Education and Cultural Integration: Strengthen multicultural education for immigrants to promote social inclusion and integration. Provide free language training to help immigrants better adapt to their new environment and enhance their employability.
- Economic Assistance: Increase economic assistance to underdeveloped regions to improve local living conditions and reduce the flow of impoverished people. Furthermore, improve social security for immigrants to help them better integrate into EU society.

